Smart Meters & Energy Management
What exactly is a smart energy meter and why does it play a key role in the energy transition? In this article, you will discover the difference from an old meter and how smart meters contribute to more efficient energy use.
Is a smart meter mandatory?
No, a smart meter is not compulsory. But: for households or companies with solar panels, a smart meter is mandatory with solar panels when you want to feed back to the grid.
If your energy meter breaks down or is replaced because it is no longer permitted, you will automatically get a smart digital meter. So it is not necessary to request a smart meter yourself. However, you can have the reading function of the GSM communication module switched off so that it becomes a normal digital meter (i.e. not a smart one). However, you will then have to report meter readings manually again. The meter will still exchange technical information with the grid operator about, for instance, the operation of the meter.
In 2026, all analogue meters will be replaced by smart or digital new meters. This will allow grid operators and energy suppliers to use a digital infrastructure for energy registration. Households or companies with solar panels must have a suitable digital meter that measures supply and returned energy separately. This is not the case with an analogue meter.
Energy optimisation and real-time insight
Want to make savings? Then insight is essential. If you have your smart meter read via P1 or app, you can see exactly how much electricity you consume and how much you feed back. Digital meters register consumption, supply and return of electricity, which is especially useful if you have solar panels. You not only see how much energy you use, but also how much you feed back to the grid. With this data, you can adjust your energy consumption by regulating appliances or switching them on or off.
Smart meter readout P1
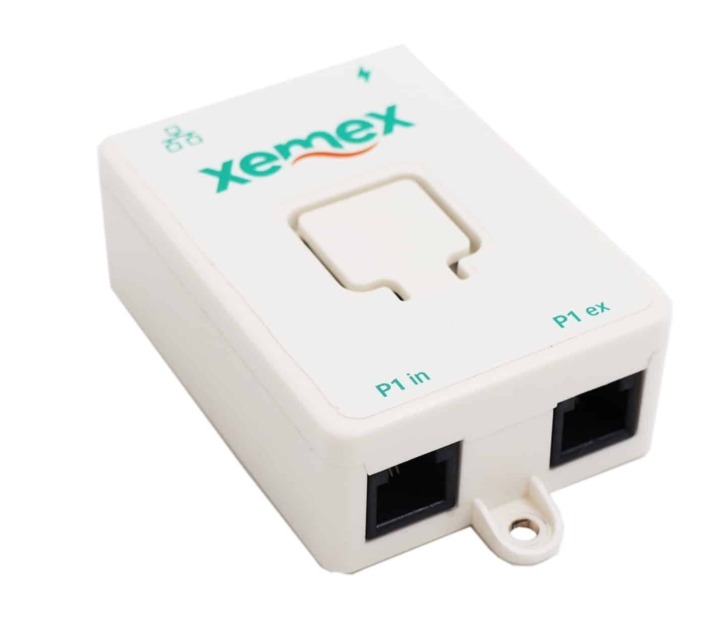
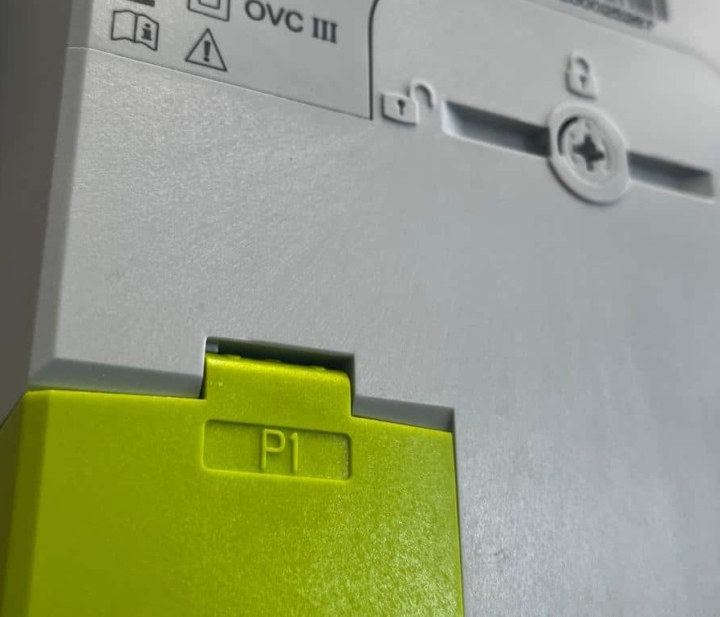
Reading out your energy consumption can be done via a smart meter app or via the P1 port of your (smart) digital meter and helps you to be more energy-conscious.
Reading via a smart meter app
A smart meter sends meter readings to your grid operator via the GSM communication module based on the reading frequency you have given permission for. The consumption data are displayed via an app or online portal of your energy supplier or an external service provider, which receives this data from your grid operator. The data shown is not real-time, but usually with a 1-day delay (for daily data) or longer for monthly readings.
Readout frequency:
- Once a year (by default without explicit consent). For the annual statement or when moving/supplier change.
- Monthly (only with permission). For consumption insight and advance payment control.
- Daily (only with explicit consent). For apps and energy consumption insight on a daily basis.
For an accurate and real-time overview of your consumption data, it is better to use the digital meter’s P1 port in combination with an energy monitoring or management system.
Efficient energy management with a smart meter
Installations with solar panels require a (smart) digital meter for solar electricity feed-in. This digital infrastructure allows you to see exactly what you consume in real time and how much you feed back to the grid, and match this to your usage for efficient energy management.
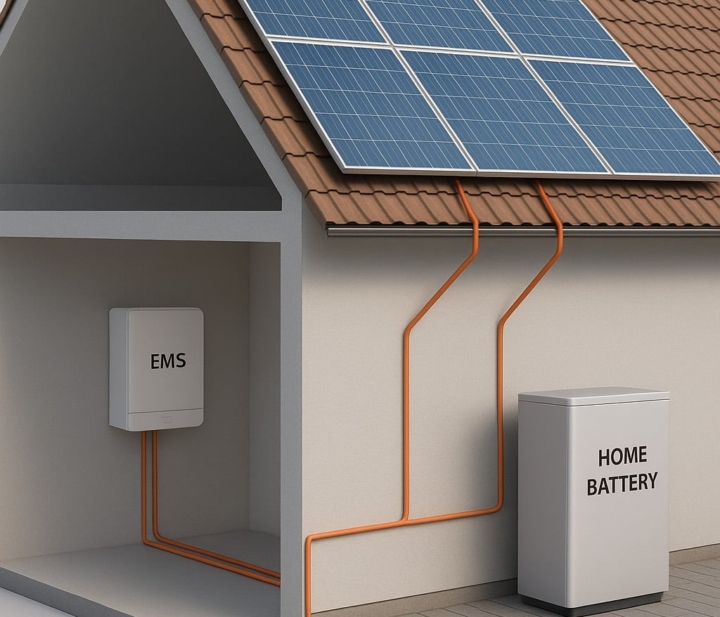
An energy management system (EMS) can use this data to maximise self-consumption of solar power. The EMS interfaces with the smart meter via the P1 port and reads real-time power consumption and feed-in. Based on this, the system can control appliances, such as automatically switching on the washing machine or dishwasher when solar power is available.
It can also activate charging stations, home batteries or an electric boiler to use excess solar power locally instead of feeding it back. This increases self-consumption of solar power and reduces dependence on the grid. In addition, the system can help prevent peak loads, which is beneficial in dynamic tariffs.
Benefits of smart meters for different user groups
Using a smart meter can bring several benefits for different groups:
- Households: real-time insight into consumption & feed-in, savings, automatic meter reading, support for dynamic tariffs.
- Housing associations: central energy monitoring and management, early detection of waste, data for sustainability requirements (e.g. BENG).
- Grid operators: quick fault detection, better grid balance, more efficient maintenance.
- Energy suppliers: automatic receipt of meter readings, consumption data for customer advice, new tariff models, improved service.
- Companies (SMEs): consumption optimisation, cost savings, support in energy management and ISO 50001 or ESG reporting.
- Governments/cooperatives: insight into local energy generation & consumption, collective data analysis, sustainability policy support.
🛠️ Practical applications
In residential areas, smart meters allow grid operators to monitor and adjust energy consumption. Property managers use the smart meter portal to analyse consumption in apartment complexes.
Individuals can easily adjust their behaviour and save via the smart meter app. With a dongle smart meter, users can easily adjust their behaviour, for example by washing outside peak hours or charging electric cars when electricity is cheapest.
For larger projects, Xemex offers complete energy infrastructure solutions scalable from homes to business parks. This includes smart sensors, data gateway solutions and integration with existing energy management systems.
⚠️ Challenges and limitations
While the smart meter offers many advantages, there are also concerns such as:
⛔ Privacy and data security: if there is insufficient security, your consumption data can give insight into your lifestyle patterns.
⚡ Dependence on mobile network: poor mobile phone coverage can interfere with data transmission.
❌ Possible measurement anomalies: different consumption readings for certain appliances with non-linear consumption (e.g. dimmers or induction hobs).
🚫 Limited data control: unclear who has access to your data. These can be used for marketing purposes.
❓ Compatibility and failures: errors in software updates (such as DSMR protocol) or incompatibility with older devices can interfere with readouts or communication.
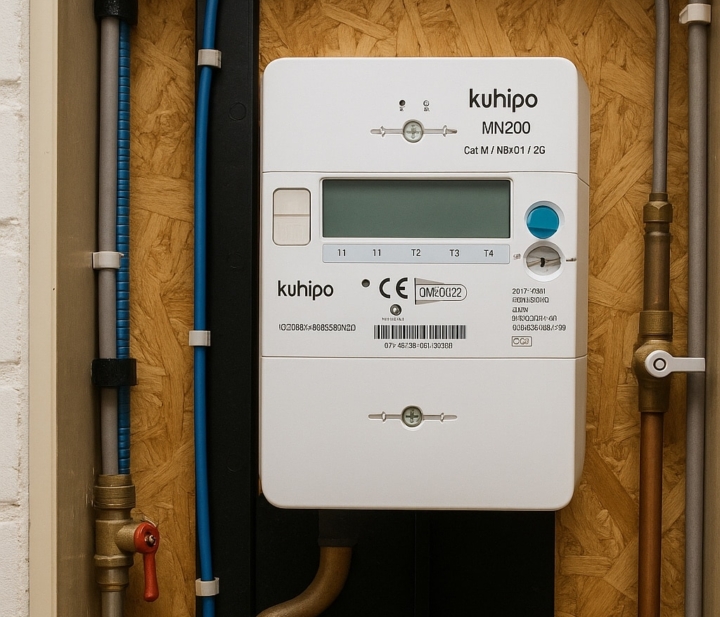
Xemex smart meter
Xemex’s smart digital meters, such as the KWHIQ series, are advanced energy meters for accurate measurement of electricity consumption and production in homes, businesses and smart grid environments alike.
- Automatic and remote reading thanks to built-in communication via 4G LTE Cat-M with 2G fallback and optional NB-IoT.
- Read real-time consumption data via P1 or optical port.
- Support protocols such as DLMS/COSEM and DSMR 5.0.2 for HEMs.
- MID-certified and developed according to IEC standards for accurate measurements.
- Remote firmware updates and parameter configuration.
- Alarm functions and security features ensure early detection of sabotage or tampering.
- Suitable for dynamic energy tariffs and support load balancing, also in combination with home batteries or smart charging stations.
- Optionally, the meters are equipped with an internal disconnector, allowing remote power on/off.
Xemex EMS system linked to smart meter
Thanks to real-time data available through the smart meter, Xemex’s Energy Management System can better match energy supply and demand.
Xemex offers the Enny EMS series for this purpose, among others: Enny Go, Enny Pro, Enny Expert and Enny Master. These systems range from simple energy consumption monitoring to advanced analysis, reporting and optimisation. This allows you to track your energy consumption in real time, link it to cost structures and even react automatically to grid conditions. Via the Enny app or dashboard, you get insight into consumption patterns and optimisations. In this way, the smart meter together with the Xemex EMS contributes to energy saving and cost reduction.
For those working with industrial applications or EV charging infrastructure, Xemex also offers the P1MB converter, which converts P1 data to Modbus RTU. This makes the system highly suitable for integration with smart grids and local energy networks.
Conclusion Smart meters
A smart meter is more than just a digital replacement for the traditional meter. It is a central player in the energy transition, aiming to provide insight into your energy consumption and enable cost savings through integrations with other systems.
Thanks to Xemex’s solutions such as the smart KWHIQ meter, Enny EMS and P1MB module, a future-proof, scalable infrastructure for any energy use is created. They play an important role in building a smart, flexible and sustainable energy network, in which measuring, controlling and automating are central.
Always ready to start
Wondering what we can do for your organization? Contact Xemex and discuss your needs with our team. Together we will realize a solution that addresses your energy challenges and opens up new possibilities.
Burgemeester Burgerslaan 40
5245 NH 's-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Metropoolstraat 11a
2900 Schoten; Belgium